Scientists Disprove Bunkbed Conjecture

Mathematicians from Russia, including two HSE graduates, have disproven a well-known mathematical conjecture that, despite lacking solid proof, had been considered valid for 40 years. The ‘Bunkbed Conjecture’ belongs to percolation theory—a branch of mathematics that studies the formation of connected structures in independent environments.
The hypothesis was proposed in the 1980s by Dutch physicist Pieter Kasteleyn, who aimed to mathematically describe how liquids seep through porous surfaces, such as water saturating a sponge.
The conjecture is based on random connections between vertices in an imaginary graph resembling a bunkbed. It posits that the probability of a connection forming between two vertices on the same level is higher than the probability of a connection forming between levels.
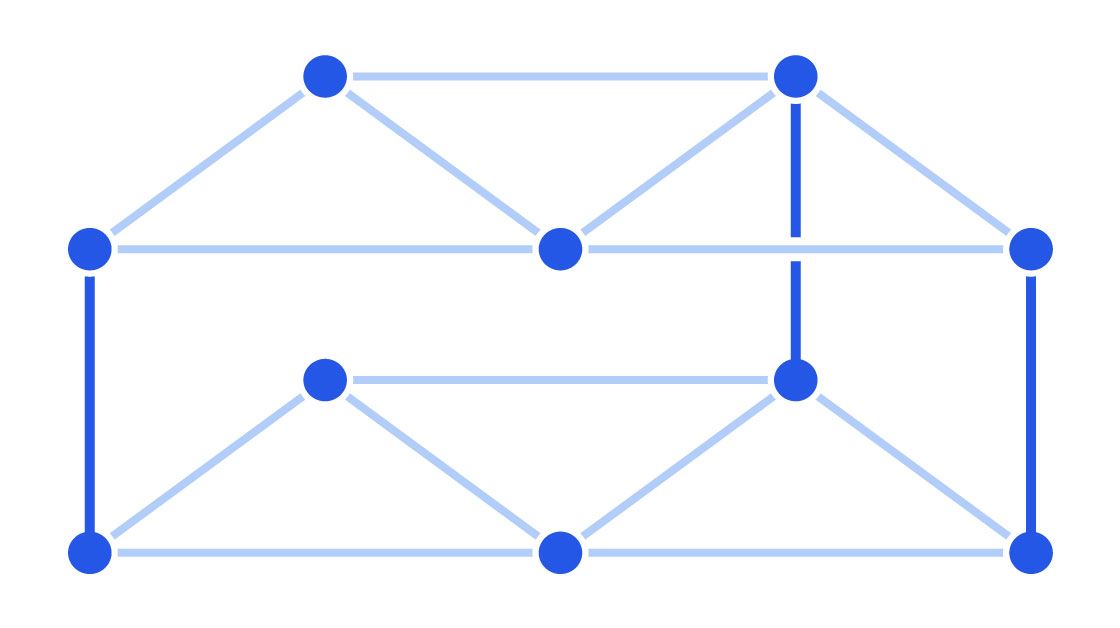
While this statement seems intuitively true, no convincing proof had been found to confirm or refute it until recently. Sceptics argued that the claim was too general to hold true in all cases.
Mathematics typically focuses on proving the validity of statements, with disproofs being relatively rare. However, a team of Russian mathematicians—Igor Pak, Nikita Gladkov, and Aleksandr Zimin—managed to find a counterexample that invalidated the conjecture.
‘Actually, my colleague Nikita Gladkov and I first encountered the “bunkbed” concept during our freshman year at HSE. We were dorm roommates, and our room actually had a bunkbed,’ joked Aleksandr Zimin. ‘With this conjecture, we understood that it holds true for most cases. But we were curious—are there rare cases where it fails?’
Initially, the team tried to find a counterexample using machine learning methods. They trained a neural network to identify potential connections in graphs and attempted to explore all possible configurations. However, for graphs with more than nine vertices, the number of possible connections grew exponentially, quickly exceeding computational limits. No proof was found.
The researchers then adapted methods from hypergraph theory, where a disproof of the Bunkbed Conjecture already existed, to classical graphs. They constructed a highly complex structure containing thousands of vertices and edges. In this graph, the probability of a connection forming between the upper and lower levels was slightly higher than the probability of a connection forming on the lower level, thereby disproving the conjecture.
‘My co-authors Igor Pak and Nikita Gladkov—who are currently working at UCLA—and I complemented each other perfectly on this project. I prefer using numerical methods. In my opinion, to truly understand a problem, you need to be able to program it and explain it to a computer. Nikita, on the other hand, takes a different approach and prefers relying on a more abstract, intuitive level,’ says Aleksandr Zimin, one of the authors of the paper and a postgraduate student at the HSE Faculty of Mathematics.

Aleksandr Zimin
‘The conjecture resisted disproof for a long time—or perhaps no one wanted to disprove it because it was beautiful and elegant. However, in my view, disproving it does not destroy its beauty; rather, it proves that the world is far more interesting and complex than we thought,’ Zimin says.
The discovered counterexample raises fundamental questions for science about whether intuition can be relied upon, how critical thinking should be applied in mathematics, and how probabilistic evidence-based proofs should be interpreted.
See also:
Scientists Discover Link Between Brain's Structural Features and Autistic Traits in Children
Scientists have discovered significant structural differences in the brain's pathways, tracts, and thalamus between children with autism and their neurotypical peers, despite finding no functional differences. The most significant alterations were found in the pathways connecting the thalamus—the brain's sensory information processing centre—to the temporal lobe. Moreover, the severity of these alterations positively correlated with the intensity of the child's autistic traits. The study findings have been published in Behavioural Brain Research.
Earnings Inequality Declining in Russia
Earnings inequality in Russia has nearly halved over the past 25 years. The primary factors driving this trend are rising minimum wages, regional economic convergence, and shifts in the returns on education. Since 2019, a new phase of this process has been observed, with inequality continuing to decline but driven by entirely different mechanisms. These are the findings made by Anna Lukyanova, Assistant Professor at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences, in her new study. The results have been published in the Journal of the New Economic Association.
Russian Physicists Discover Method to Increase Number of Atoms in Quantum Sensors
Physicists from the Institute of Spectroscopy of the Russian Academy of Sciences and HSE University have successfully trapped rubidium-87 atoms for over four seconds. Their method can help improve the accuracy of quantum sensors, where both the number of trapped atoms and the trapping time are crucial. Such quantum systems are used to study dark matter, refine navigation systems, and aid in mineral exploration. The study findings have been published in the Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics Letters.
HSE Scientists Develop Application for Diagnosing Aphasia
Specialists at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain have developed an application for diagnosing language disorders (aphasia), which can result from head injuries, strokes, or other neurological conditions. AutoRAT is the first standardised digital tool in Russia for assessing the presence and severity of language disorders. The application is available on RuStore and can be used on mobile and tablet devices running the Android operating system.
HSE Researchers Discover Simple and Reliable Way to Understand How People Perceive Taste
A team of scientists from the HSE Centre for Cognition & Decision Making has studied how food flavours affect brain activity, facial muscles, and emotions. Using near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS), they demonstrated that pleasant food activates brain areas associated with positive emotions, while neutral food stimulates regions linked to negative emotions and avoidance. This approach offers a simpler way to predict the market success of products and study eating disorders. The study was published in the journal Food Quality and Preference.
Russian Scientists Demonstrate How Disorder Contributes to Emergence of Unusual Superconductivity
Researchers at HSE University and MIPT have investigated how the composition of electrons in a superconductor influences the emergence of intertype superconductivity—a unique state in which superconductors display unusual properties. It was previously believed that intertype superconductivity occurs only in materials with minimal impurities. However, the scientists discovered that the region of intertype superconductivity not only persists but can also expand in materials with a high concentration of impurities and defects. In the future, these superconductors could contribute to the development of highly sensitive sensors and detectors. The study has been published in Frontiers of Physics.
HSE Scientists Take Important Step Forward in Development of 6G Communication Technologies
Researchers at HSE MIEM have successfully demonstrated the effective operation of a 6G wireless communication channel at sub-THz frequencies. The device transmits data at 12 Gbps and maintains signal stability by automatically switching when blocked. These metrics comply with international 6G standards. An article published on arXiv, an open-access electronic repository, provides a description of certain elements of the system.
AI vs AI: Scientists Develop Neural Networks to Detect Generated Text Insertions
A research team, including Alexander Shirnin from HSE University, has developed two models designed to detect AI-generated insertions in scientific texts. The AIpom system integrates two types of models: a decoder and an encoder. The Papilusion system is designed to detect modifications through synonyms and summarisation by neural networks, using one type of models: encoders. In the future, these models will assist in verifying the originality and credibility of scientific publications. Articles describing the Papilusion and AIpom systems have been published in the ACL Anthology Digital Archive.
Acoustic Battles for the Harem: How the Calls of Siberian Wapiti Reveal Their Status and Individuality
Researchers at HSE University, Lomonosov Moscow State University, and the A.N. Severtsov Institute of Ecology and Evolution of the Russian Academy of Sciences have studied the distinctive vocalisations of Siberian wapiti (Cervus canadensis sibiricus) stags during the peak of the mating season, when males produce rutting calls (bugles) to attract females (hinds) and deter rivals. The scientists have discovered how the acoustic parameters of these rutting calls reflect the stag's status—whether he currently holds a harem or is still attempting to acquire one—as well as his individual characteristics. The study has been published in Journal of Zoology.
Z-Flipons: How Specific DNA Regions Help Regulate Gene Function
Researchers at HSE University and InsideOutBio have applied machine learning to identify the location and functions of mirror-twisted DNA structures, known as Z-flipons, in human and mouse genomes. The scientists discovered which Z-DNA regions were conserved in both species throughout evolution and demonstrated for the first time that Z-DNA accelerates the process of creating RNA copies of genes. The findings will contribute to the development of new treatments for genetic diseases. The study has been published in Scientific Reports.